Well, let me tell you something about this plant tissue culture thing that is going on around Africa. It’s all about growing plants in special ways, in controlled environments, where they don’t get dirty and can grow real strong. They take bits of the plant, maybe a little leaf or a stem, and put it in a kind of special soup, full of nutrients, so the plant can grow without having to go in the dirt. It’s like giving it a perfect little house to live in, where it gets all the food it needs.
Now, this plant tissue culture stuff, it’s been really taking off in places like Ethiopia. Over there, both the government and private companies are working on it, trying to figure out how to grow plants faster, stronger, and better. They use tissue culture for all sorts of crops, especially those that are important to the local farmers, like those cassavas and bananas. You see, in Africa, growing good crops is serious business, and this method helps make sure the plants don’t get sick, grow faster, and make more food for the people.
To put it simply, tissue culture is just like a fancy way of making sure plants get everything they need without them being bothered by pests or diseases. Imagine you’re in the middle of a drought, and your regular crops might not survive. But, if you can take a tiny piece of a plant and grow it in a nice, safe place, you’ve got a backup plan! This is especially useful for farmers who need to keep their crops going, even when the weather isn’t being kind.
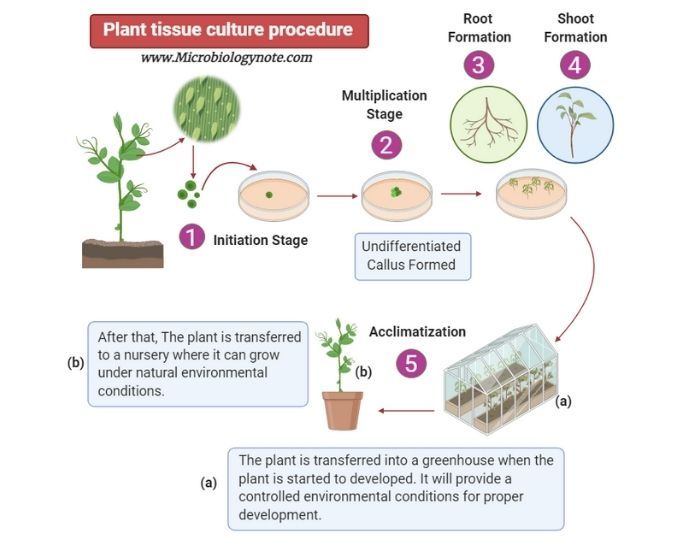
There are different kinds of tissue culture methods, but the basic idea is the same everywhere: you take a little bit of the plant, put it in a nutrient-rich solution, and keep it in a clean, controlled environment. That’s it! No dirt, no pests, just the plant, food, and air to help it grow. And believe me, it works wonders. Not just in Africa, but all around the world. From bananas to coffee to even cassava, it’s been a real game-changer for farming folks.
Why does this matter to Africa?
Well, Africa is a huge continent, and not all the land is fertile or easy to farm. Sometimes, the soil’s not so good, and the weather can be harsh. So, having a way to grow plants without needing a big piece of land, and without worrying about pests or diseases, is a big deal. That’s where tissue culture comes in. It gives farmers a way to grow more food in less time, with fewer worries about the plants getting sick or eaten by bugs.
What’s more, the method doesn’t just help the farmers with their current crops, it can also help improve crops over time. Through tissue culture, researchers can take plants and change them to be stronger, better at resisting pests, or more nutritious. That’s right, folks, the plants can get better by just tweaking a few things in the lab. It’s like giving a plant a little upgrade! And in places like Ethiopia, they’ve been using this to help grow crops that are hardier and more reliable, so farmers don’t lose everything when the weather turns bad.
But how does it work, exactly?
It starts with the plant. Researchers go out and pick a part of the plant, something that can grow into a new plant on its own. Then, they sterilize it, making sure it doesn’t have any bacteria or fungi on it. After that, they put the plant piece in a nutrient-rich liquid or gel, something that has all the vitamins and minerals the plant needs to grow strong and healthy.
Then, it’s time for the waiting game. The plant needs time to grow, just like when you plant seeds in the ground. The difference is, this happens inside a controlled environment where the temperature, light, and air are just right. After a while, the little plant starts to grow bigger and stronger. Once it’s big enough, it can be planted out in the field, ready to produce food for the people!
Benefits of Tissue Culture in Africa:
- Better Crop Yields: With tissue culture, crops grow faster and produce more, which means more food for everyone.
- Stronger Plants: These plants are more resistant to pests and diseases, which means less loss for farmers.
- Faster Growth: Plants can grow quicker, so farmers can get crops faster and grow more in one season.
- Less Need for Land: You don’t need a huge plot of land to grow a lot of plants. Just a little bit of space for the tissue culture process can lead to a lot of plants.
- Improvement of Local Crops: Scientists are always working to make local crops better, more nutritious, and more productive.
But, it’s not just about making plants grow. This tissue culture business is also about keeping the environment safe. By using tissue culture, they don’t need as many chemicals or pesticides to keep the plants healthy, which is better for the land and the people living on it. Less pollution, less harm to the land, and better crops. It’s a win-win!
So, you see, this plant tissue culture thing is more than just science. It’s about helping the farmers, improving the crops, and making sure the people in Africa have enough food to eat, no matter what the weather does. It’s about using a little bit of knowledge and a whole lot of care to make the world a better place for everyone, one plant at a time.
Tags:[plant tissue culture, tissue culture in Africa, crop improvement, Ethiopia farming, African agriculture, tissue culture technology, plant propagation, genetic improvement, African crops, farming innovations]